WILDFIRES AFFECT DOMESTIC AIR QUALITY
입력 2020.01.17 (14:58)
수정 2020.01.17 (16:47)
읽어주기 기능은 크롬기반의
브라우저에서만 사용하실 수 있습니다.
[Anchor Lead]
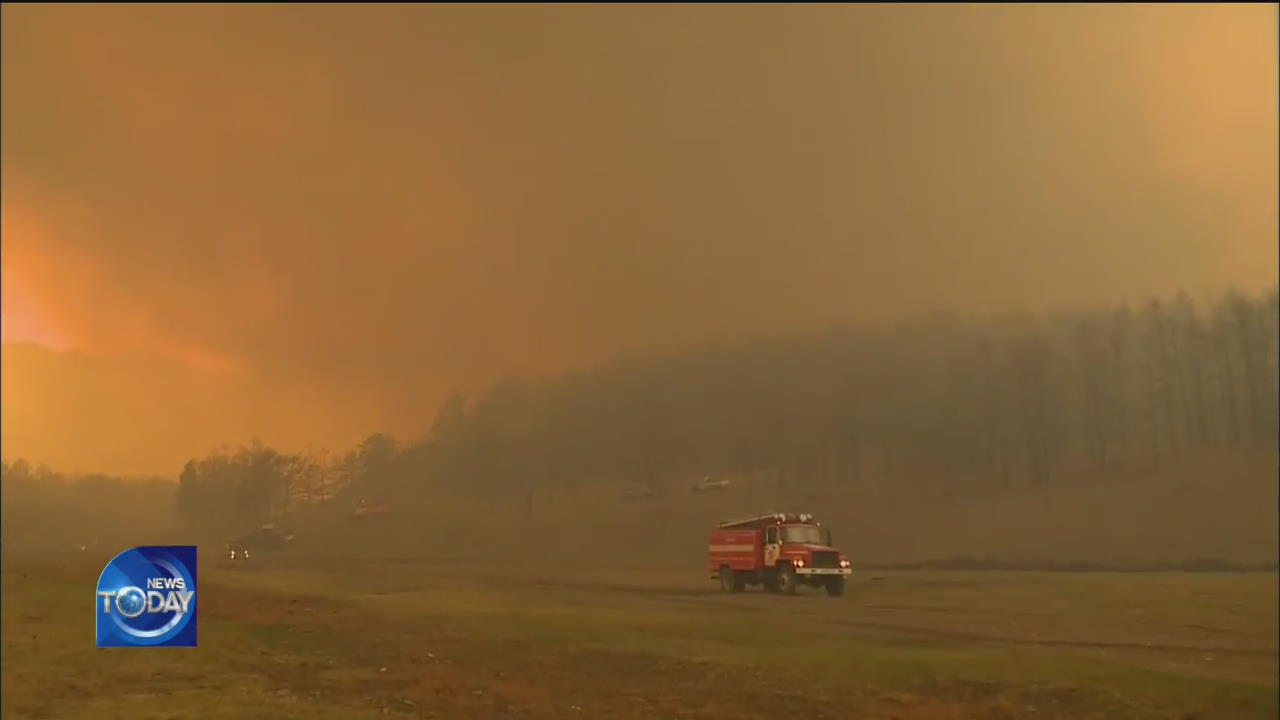
Due to global warming, various parts of the globe are struggling with wildfires such as Australia and Siberia. A recent study by experts has found that microdust emitted from wildfires in Siberia is affecting air quality in Korea.
[Pkg]
A vast field in Siberia is blanketed with smoke. Two massive wildfires that occurred here last year burned down an area equaling a third of Korea's land mass. Wildfires in Siberia have become more frequent and larger in scale each year. A study conducted by Korean researchers concluded that the trend in Siberia is becoming more palpable because of global warming. The study has revealed that the higher the February and March temperatures are in Siberia, the more frequently the region is affected by wildfires in April and May, as snow melts faster, creating dry conditions.
[Soundbite] KOOK JONG-SUNG(POSTECH) : "As global warming progresses, inland areas become warmer and drier and snow melts faster, which may result in stronger wildfires."
A layer of permafrost beneath the ground in Siberia contains large amounts of carbon. The researchers warn that carbon emitted from the permafrost layer could exacerbate global warming. Wildfires in Siberia are also affecting the air quality on the Korean Peninsula. The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science has found that three or four days after wildfires broke in Siberia, microdust levels in the city of Daejeon soared to the "bad" level. An analysis of air particles revealed that the concentration of levoglucosan, which is emitted by burning wood, was 4.5 times the normal level.
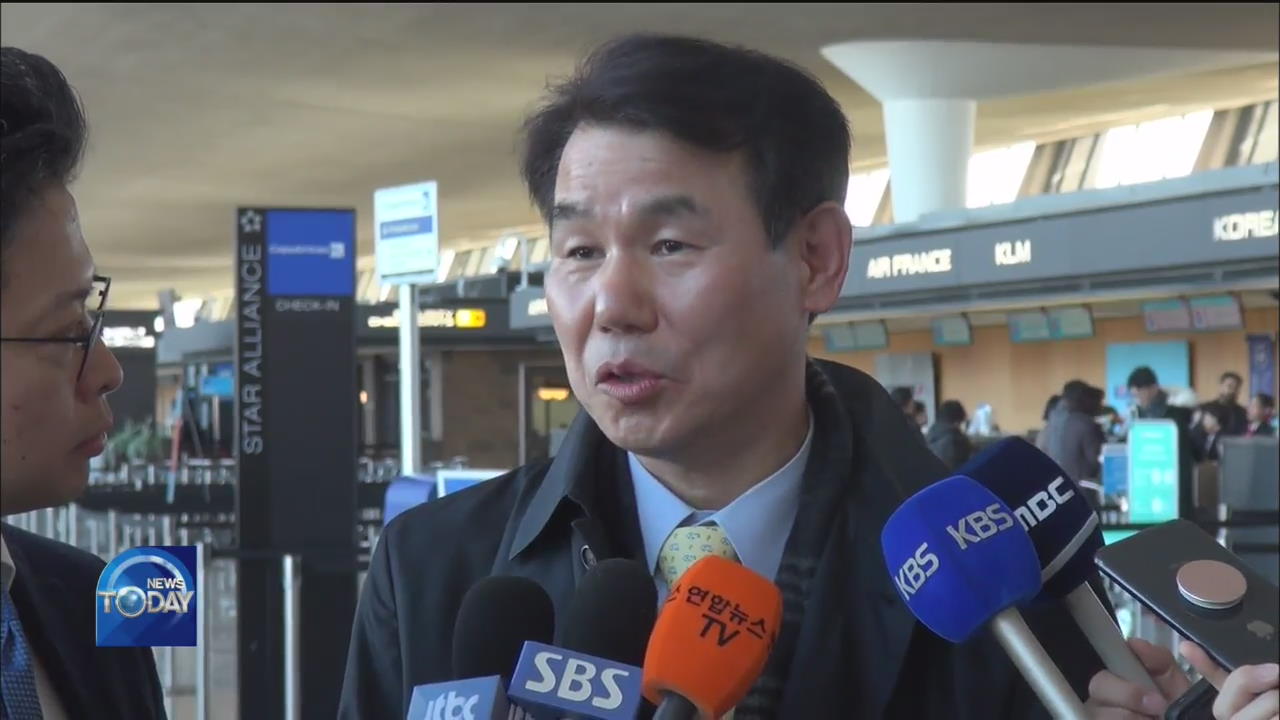
[Soundbite] CHUNG JIN-SANG(PH.D., KOREA RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND SCIENCE) : "We have proved scientifically that microdust emitted from the surging amounts of levoglucosan during Siberian wildfires affected air quality on the Korean Peninsula."
Wildfires caused by climate change as a result of human activity are now threatening the very human existence by polluting the air we breathe.
Due to global warming, various parts of the globe are struggling with wildfires such as Australia and Siberia. A recent study by experts has found that microdust emitted from wildfires in Siberia is affecting air quality in Korea.
[Pkg]
A vast field in Siberia is blanketed with smoke. Two massive wildfires that occurred here last year burned down an area equaling a third of Korea's land mass. Wildfires in Siberia have become more frequent and larger in scale each year. A study conducted by Korean researchers concluded that the trend in Siberia is becoming more palpable because of global warming. The study has revealed that the higher the February and March temperatures are in Siberia, the more frequently the region is affected by wildfires in April and May, as snow melts faster, creating dry conditions.
[Soundbite] KOOK JONG-SUNG(POSTECH) : "As global warming progresses, inland areas become warmer and drier and snow melts faster, which may result in stronger wildfires."
A layer of permafrost beneath the ground in Siberia contains large amounts of carbon. The researchers warn that carbon emitted from the permafrost layer could exacerbate global warming. Wildfires in Siberia are also affecting the air quality on the Korean Peninsula. The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science has found that three or four days after wildfires broke in Siberia, microdust levels in the city of Daejeon soared to the "bad" level. An analysis of air particles revealed that the concentration of levoglucosan, which is emitted by burning wood, was 4.5 times the normal level.
[Soundbite] CHUNG JIN-SANG(PH.D., KOREA RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND SCIENCE) : "We have proved scientifically that microdust emitted from the surging amounts of levoglucosan during Siberian wildfires affected air quality on the Korean Peninsula."
Wildfires caused by climate change as a result of human activity are now threatening the very human existence by polluting the air we breathe.
■ 제보하기
▷ 카카오톡 : 'KBS제보' 검색, 채널 추가
▷ 전화 : 02-781-1234, 4444
▷ 이메일 : kbs1234@kbs.co.kr
▷ 유튜브, 네이버, 카카오에서도 KBS뉴스를 구독해주세요!
- WILDFIRES AFFECT DOMESTIC AIR QUALITY
-
- 입력 2020-01-17 15:00:43
- 수정2020-01-17 16:47:30

[Anchor Lead]
Due to global warming, various parts of the globe are struggling with wildfires such as Australia and Siberia. A recent study by experts has found that microdust emitted from wildfires in Siberia is affecting air quality in Korea.
[Pkg]
A vast field in Siberia is blanketed with smoke. Two massive wildfires that occurred here last year burned down an area equaling a third of Korea's land mass. Wildfires in Siberia have become more frequent and larger in scale each year. A study conducted by Korean researchers concluded that the trend in Siberia is becoming more palpable because of global warming. The study has revealed that the higher the February and March temperatures are in Siberia, the more frequently the region is affected by wildfires in April and May, as snow melts faster, creating dry conditions.
[Soundbite] KOOK JONG-SUNG(POSTECH) : "As global warming progresses, inland areas become warmer and drier and snow melts faster, which may result in stronger wildfires."
A layer of permafrost beneath the ground in Siberia contains large amounts of carbon. The researchers warn that carbon emitted from the permafrost layer could exacerbate global warming. Wildfires in Siberia are also affecting the air quality on the Korean Peninsula. The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science has found that three or four days after wildfires broke in Siberia, microdust levels in the city of Daejeon soared to the "bad" level. An analysis of air particles revealed that the concentration of levoglucosan, which is emitted by burning wood, was 4.5 times the normal level.
[Soundbite] CHUNG JIN-SANG(PH.D., KOREA RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND SCIENCE) : "We have proved scientifically that microdust emitted from the surging amounts of levoglucosan during Siberian wildfires affected air quality on the Korean Peninsula."
Wildfires caused by climate change as a result of human activity are now threatening the very human existence by polluting the air we breathe.
Due to global warming, various parts of the globe are struggling with wildfires such as Australia and Siberia. A recent study by experts has found that microdust emitted from wildfires in Siberia is affecting air quality in Korea.
[Pkg]
A vast field in Siberia is blanketed with smoke. Two massive wildfires that occurred here last year burned down an area equaling a third of Korea's land mass. Wildfires in Siberia have become more frequent and larger in scale each year. A study conducted by Korean researchers concluded that the trend in Siberia is becoming more palpable because of global warming. The study has revealed that the higher the February and March temperatures are in Siberia, the more frequently the region is affected by wildfires in April and May, as snow melts faster, creating dry conditions.
[Soundbite] KOOK JONG-SUNG(POSTECH) : "As global warming progresses, inland areas become warmer and drier and snow melts faster, which may result in stronger wildfires."
A layer of permafrost beneath the ground in Siberia contains large amounts of carbon. The researchers warn that carbon emitted from the permafrost layer could exacerbate global warming. Wildfires in Siberia are also affecting the air quality on the Korean Peninsula. The Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science has found that three or four days after wildfires broke in Siberia, microdust levels in the city of Daejeon soared to the "bad" level. An analysis of air particles revealed that the concentration of levoglucosan, which is emitted by burning wood, was 4.5 times the normal level.
[Soundbite] CHUNG JIN-SANG(PH.D., KOREA RESEARCH INSTITUTE OF STANDARDS AND SCIENCE) : "We have proved scientifically that microdust emitted from the surging amounts of levoglucosan during Siberian wildfires affected air quality on the Korean Peninsula."
Wildfires caused by climate change as a result of human activity are now threatening the very human existence by polluting the air we breathe.
이 기사가 좋으셨다면
-
좋아요
0
-
응원해요
0
-
후속 원해요
0
















이 기사에 대한 의견을 남겨주세요.