Pollution Analysis
입력 2019.03.19 (15:26)
수정 2019.03.19 (15:40)
읽어주기 기능은 크롬기반의
브라우저에서만 사용하실 수 있습니다.
[Anchor Lead]
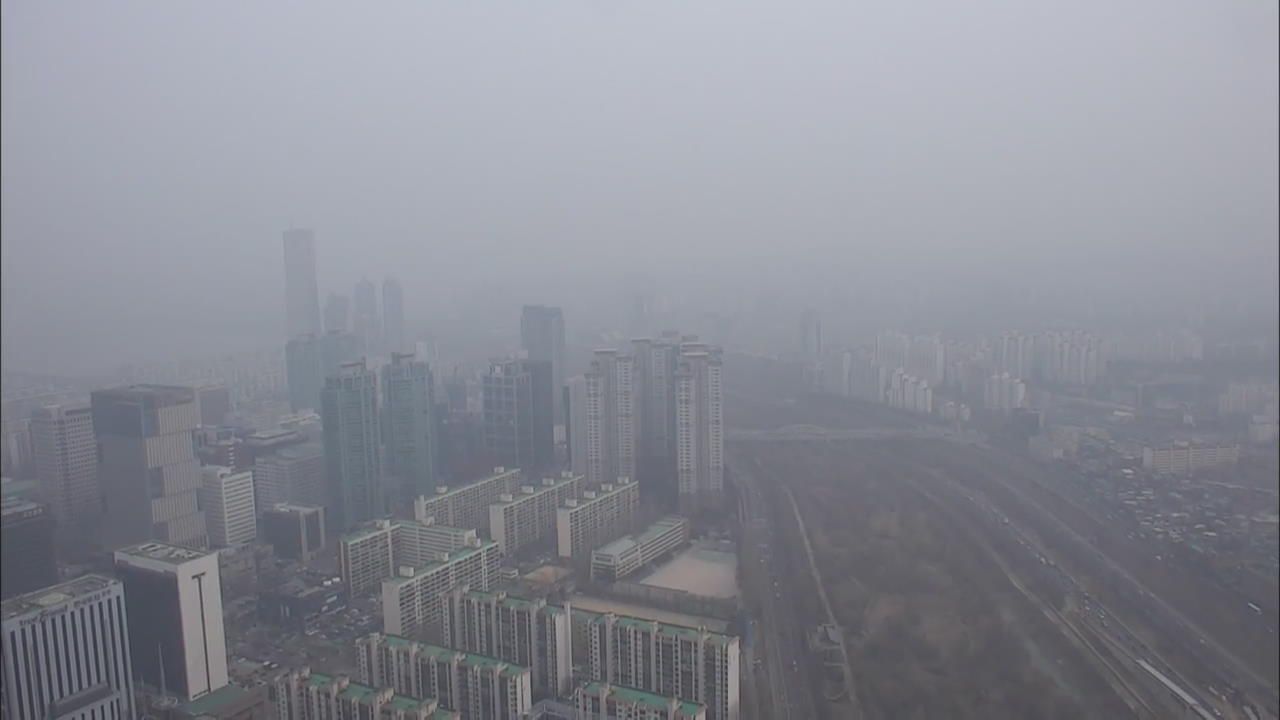
The severe air pollution in Korea early this month was largely caused by poor air quality in China. An analysis conducted by experts at the request of KBS has revealed that China-caused dust accounts for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea.
[Pkg]
High-concentration level of fine dust blanketed Korea for over a week as we approached Spring. The average daily concentration in Seoul recorded 135 ㎍/㎥. In Sejong, an all time high of 143 ㎍/㎥. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory of Seoul National University conducted an air quality analysis. The results of simulation tests showed dust originating from China accounted for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea. The main culprits were the Shandong Peninsula, located close to Korea and China's northern regions where many large cities like Beijing are located. Pollutants from that country repeatedly accumulated in the skies over the Korean Peninsula because no wind was blowing at the time. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory also analyzed for the first time the composition of fine dust particles. Ammonium nitrate was found to make up more than 70 percent of the dust. The substance is formed through a combination of emissions from diesel vehicles in large cities and ammonia emitted in agricultural areas.
[Soundbite] Prof. Park Rok-jin(Seoul National University) : "Nitrogen compounds and ammonia originating from China form ammonium nitrate, which subsequently permeates Korea and affects its air quality."
Experts point out that diesel car emissions are more toxic and detrimental to health than those emitted by factories or power plants, even when the concentration levels are similar.
The severe air pollution in Korea early this month was largely caused by poor air quality in China. An analysis conducted by experts at the request of KBS has revealed that China-caused dust accounts for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea.
[Pkg]
High-concentration level of fine dust blanketed Korea for over a week as we approached Spring. The average daily concentration in Seoul recorded 135 ㎍/㎥. In Sejong, an all time high of 143 ㎍/㎥. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory of Seoul National University conducted an air quality analysis. The results of simulation tests showed dust originating from China accounted for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea. The main culprits were the Shandong Peninsula, located close to Korea and China's northern regions where many large cities like Beijing are located. Pollutants from that country repeatedly accumulated in the skies over the Korean Peninsula because no wind was blowing at the time. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory also analyzed for the first time the composition of fine dust particles. Ammonium nitrate was found to make up more than 70 percent of the dust. The substance is formed through a combination of emissions from diesel vehicles in large cities and ammonia emitted in agricultural areas.
[Soundbite] Prof. Park Rok-jin(Seoul National University) : "Nitrogen compounds and ammonia originating from China form ammonium nitrate, which subsequently permeates Korea and affects its air quality."
Experts point out that diesel car emissions are more toxic and detrimental to health than those emitted by factories or power plants, even when the concentration levels are similar.
■ 제보하기
▷ 카카오톡 : 'KBS제보' 검색, 채널 추가
▷ 전화 : 02-781-1234, 4444
▷ 이메일 : kbs1234@kbs.co.kr
▷ 유튜브, 네이버, 카카오에서도 KBS뉴스를 구독해주세요!
- Pollution Analysis
-
- 입력 2019-03-19 15:35:32
- 수정2019-03-19 15:40:23

[Anchor Lead]
The severe air pollution in Korea early this month was largely caused by poor air quality in China. An analysis conducted by experts at the request of KBS has revealed that China-caused dust accounts for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea.
[Pkg]
High-concentration level of fine dust blanketed Korea for over a week as we approached Spring. The average daily concentration in Seoul recorded 135 ㎍/㎥. In Sejong, an all time high of 143 ㎍/㎥. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory of Seoul National University conducted an air quality analysis. The results of simulation tests showed dust originating from China accounted for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea. The main culprits were the Shandong Peninsula, located close to Korea and China's northern regions where many large cities like Beijing are located. Pollutants from that country repeatedly accumulated in the skies over the Korean Peninsula because no wind was blowing at the time. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory also analyzed for the first time the composition of fine dust particles. Ammonium nitrate was found to make up more than 70 percent of the dust. The substance is formed through a combination of emissions from diesel vehicles in large cities and ammonia emitted in agricultural areas.
[Soundbite] Prof. Park Rok-jin(Seoul National University) : "Nitrogen compounds and ammonia originating from China form ammonium nitrate, which subsequently permeates Korea and affects its air quality."
Experts point out that diesel car emissions are more toxic and detrimental to health than those emitted by factories or power plants, even when the concentration levels are similar.
The severe air pollution in Korea early this month was largely caused by poor air quality in China. An analysis conducted by experts at the request of KBS has revealed that China-caused dust accounts for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea.
[Pkg]
High-concentration level of fine dust blanketed Korea for over a week as we approached Spring. The average daily concentration in Seoul recorded 135 ㎍/㎥. In Sejong, an all time high of 143 ㎍/㎥. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory of Seoul National University conducted an air quality analysis. The results of simulation tests showed dust originating from China accounted for more than 60 percent of air pollution in Korea. The main culprits were the Shandong Peninsula, located close to Korea and China's northern regions where many large cities like Beijing are located. Pollutants from that country repeatedly accumulated in the skies over the Korean Peninsula because no wind was blowing at the time. The Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Laboratory also analyzed for the first time the composition of fine dust particles. Ammonium nitrate was found to make up more than 70 percent of the dust. The substance is formed through a combination of emissions from diesel vehicles in large cities and ammonia emitted in agricultural areas.
[Soundbite] Prof. Park Rok-jin(Seoul National University) : "Nitrogen compounds and ammonia originating from China form ammonium nitrate, which subsequently permeates Korea and affects its air quality."
Experts point out that diesel car emissions are more toxic and detrimental to health than those emitted by factories or power plants, even when the concentration levels are similar.
이 기사가 좋으셨다면
-
좋아요
0
-
응원해요
0
-
후속 원해요
0














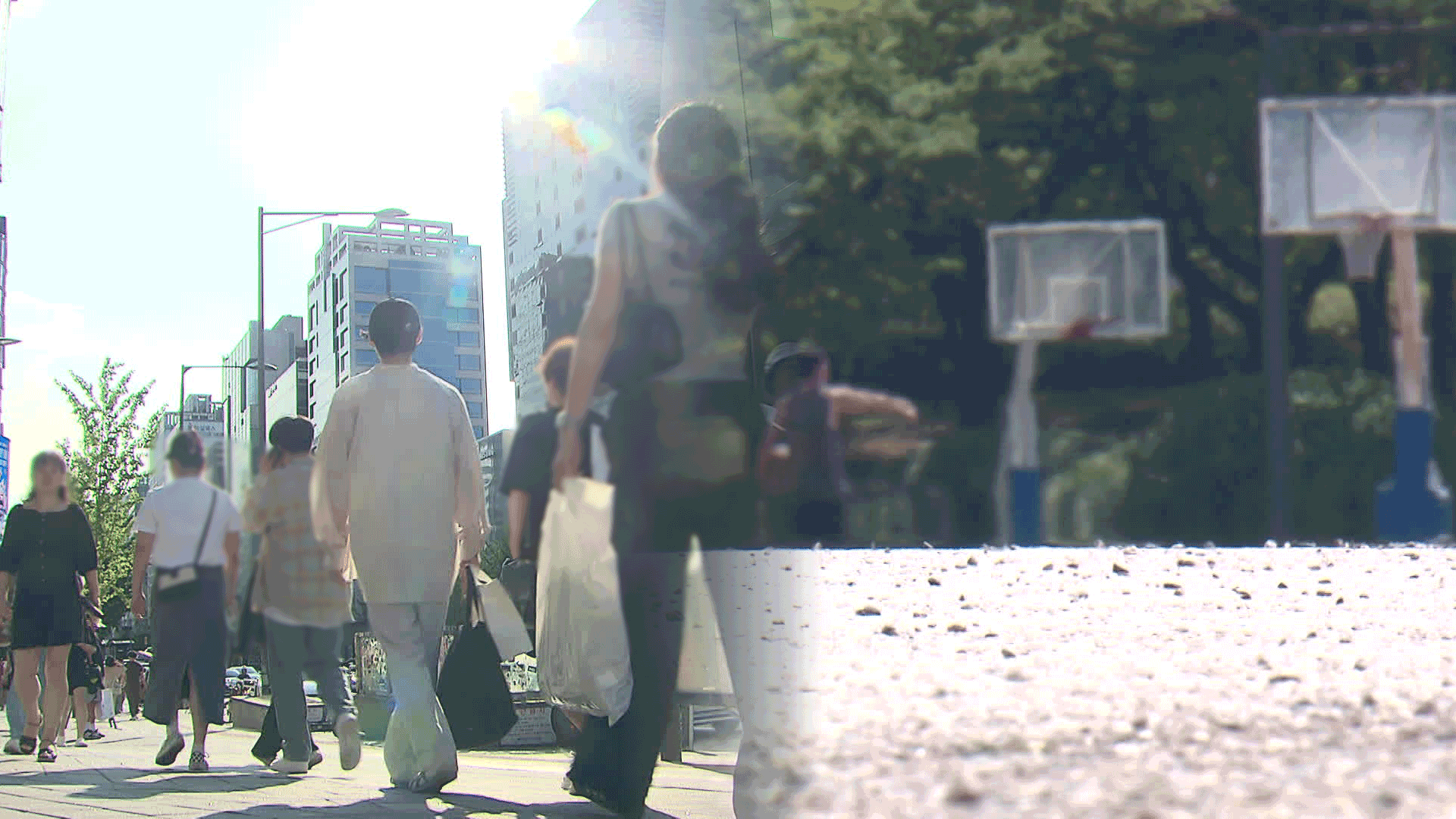

이 기사에 대한 의견을 남겨주세요.