DNA ANALYSIS OF ANCIENT KOREANS
입력 2022.06.23 (15:02)
수정 2022.06.23 (16:45)
읽어주기 기능은 크롬기반의
브라우저에서만 사용하실 수 있습니다.
[Anchor Lead]
A DNA analysis of people from the ancient Gaya Kingdom shows their genes were similar to those of modern-day Koreans. The finding has led researchers to presume that Koreans' genetic identity originates from the Three Kingdoms era.
[Pkg]
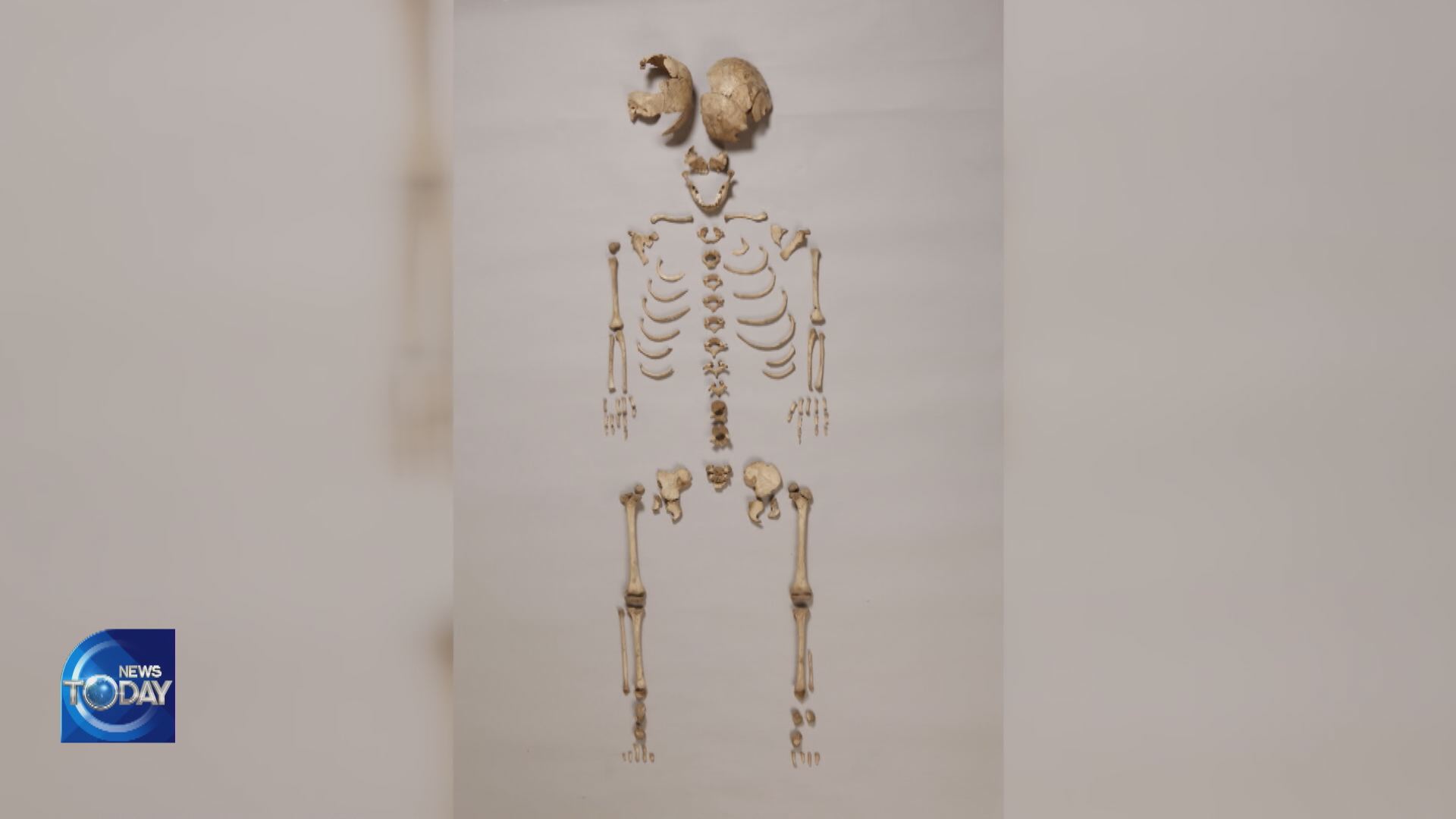
Remains that were discovered in 2019 in ancient tombs and relics sites in Gimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do Province are presumed to belong to the people who had lived in the Geumgwan Gaya period between the third and the fifth centuries A.D. The Genome Center of the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology and the University of Vienna in Austria have jointly extracted DNA from the bone and teeth samples of 22 ancient people and decoded their sequencing data. A high-quality genome data analysis of eight people showed that six of them had similar genetic information as modern-day Koreans. The finding means that Koreans' genetic continuity such as dry earwax and less severe body odor dates back to the Three Kingdoms era and has remained unchanged to this day. A montage prediction based on genome data shows that ancient people from that era looked very much like today's Koreans.
[Soundbite] Jeon Sung-won(Doctor of Bioinformatics) : "The genetic similarities include brown hair and brown eyes. It means that the genetic difference is not that big."
It's the first genome analysis of people who lived in the Three Kingdoms era. It serves as a reason to presume that the Koreans' identity was established during that time.
[Soundbite] Asta(UNIST Researcher)
The findings have been published in the international academic journal "Current Biology."
A DNA analysis of people from the ancient Gaya Kingdom shows their genes were similar to those of modern-day Koreans. The finding has led researchers to presume that Koreans' genetic identity originates from the Three Kingdoms era.
[Pkg]
Remains that were discovered in 2019 in ancient tombs and relics sites in Gimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do Province are presumed to belong to the people who had lived in the Geumgwan Gaya period between the third and the fifth centuries A.D. The Genome Center of the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology and the University of Vienna in Austria have jointly extracted DNA from the bone and teeth samples of 22 ancient people and decoded their sequencing data. A high-quality genome data analysis of eight people showed that six of them had similar genetic information as modern-day Koreans. The finding means that Koreans' genetic continuity such as dry earwax and less severe body odor dates back to the Three Kingdoms era and has remained unchanged to this day. A montage prediction based on genome data shows that ancient people from that era looked very much like today's Koreans.
[Soundbite] Jeon Sung-won(Doctor of Bioinformatics) : "The genetic similarities include brown hair and brown eyes. It means that the genetic difference is not that big."
It's the first genome analysis of people who lived in the Three Kingdoms era. It serves as a reason to presume that the Koreans' identity was established during that time.
[Soundbite] Asta(UNIST Researcher)
The findings have been published in the international academic journal "Current Biology."
■ 제보하기
▷ 카카오톡 : 'KBS제보' 검색, 채널 추가
▷ 전화 : 02-781-1234, 4444
▷ 이메일 : kbs1234@kbs.co.kr
▷ 유튜브, 네이버, 카카오에서도 KBS뉴스를 구독해주세요!
- DNA ANALYSIS OF ANCIENT KOREANS
-
- 입력 2022-06-23 15:02:56
- 수정2022-06-23 16:45:09
[Anchor Lead]
A DNA analysis of people from the ancient Gaya Kingdom shows their genes were similar to those of modern-day Koreans. The finding has led researchers to presume that Koreans' genetic identity originates from the Three Kingdoms era.
[Pkg]
Remains that were discovered in 2019 in ancient tombs and relics sites in Gimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do Province are presumed to belong to the people who had lived in the Geumgwan Gaya period between the third and the fifth centuries A.D. The Genome Center of the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology and the University of Vienna in Austria have jointly extracted DNA from the bone and teeth samples of 22 ancient people and decoded their sequencing data. A high-quality genome data analysis of eight people showed that six of them had similar genetic information as modern-day Koreans. The finding means that Koreans' genetic continuity such as dry earwax and less severe body odor dates back to the Three Kingdoms era and has remained unchanged to this day. A montage prediction based on genome data shows that ancient people from that era looked very much like today's Koreans.
[Soundbite] Jeon Sung-won(Doctor of Bioinformatics) : "The genetic similarities include brown hair and brown eyes. It means that the genetic difference is not that big."
It's the first genome analysis of people who lived in the Three Kingdoms era. It serves as a reason to presume that the Koreans' identity was established during that time.
[Soundbite] Asta(UNIST Researcher)
The findings have been published in the international academic journal "Current Biology."
A DNA analysis of people from the ancient Gaya Kingdom shows their genes were similar to those of modern-day Koreans. The finding has led researchers to presume that Koreans' genetic identity originates from the Three Kingdoms era.
[Pkg]
Remains that were discovered in 2019 in ancient tombs and relics sites in Gimhae, Gyeongsangnam-do Province are presumed to belong to the people who had lived in the Geumgwan Gaya period between the third and the fifth centuries A.D. The Genome Center of the Ulsan National Institute of Science and Technology and the University of Vienna in Austria have jointly extracted DNA from the bone and teeth samples of 22 ancient people and decoded their sequencing data. A high-quality genome data analysis of eight people showed that six of them had similar genetic information as modern-day Koreans. The finding means that Koreans' genetic continuity such as dry earwax and less severe body odor dates back to the Three Kingdoms era and has remained unchanged to this day. A montage prediction based on genome data shows that ancient people from that era looked very much like today's Koreans.
[Soundbite] Jeon Sung-won(Doctor of Bioinformatics) : "The genetic similarities include brown hair and brown eyes. It means that the genetic difference is not that big."
It's the first genome analysis of people who lived in the Three Kingdoms era. It serves as a reason to presume that the Koreans' identity was established during that time.
[Soundbite] Asta(UNIST Researcher)
The findings have been published in the international academic journal "Current Biology."
이 기사가 좋으셨다면
-
좋아요
0
-
응원해요
0
-
후속 원해요
0















이 기사에 대한 의견을 남겨주세요.