Record high greenhouse gas emissions linked to large wildfires driven by global warming
입력 2024.10.28 (23:48)
읽어주기 기능은 크롬기반의
브라우저에서만 사용하실 수 있습니다.
[Anchor]
Last year, the global concentration of greenhouse gases reached a record high once again.
It has been analyzed that large wildfires caused by the effects of global warming around the world were the main reason, and the World Meteorological Organization has warned that we are facing a vicious cycle.
Our weather expert Kim Se-hyun reports.
[Report]
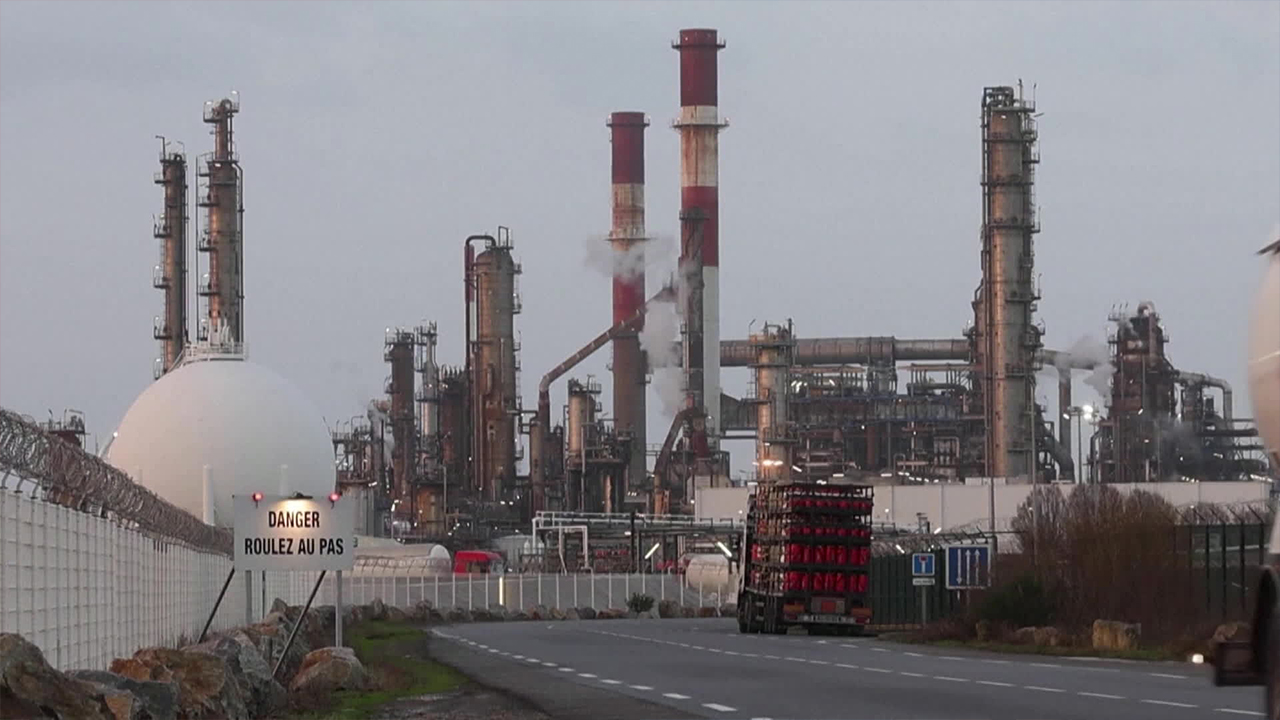
Despite global reduction efforts, greenhouse gases have increased again.
The concentration of carbon dioxide, a representative greenhouse gas, was 420 ppm last year, an increase of 2.3 ppm from the previous year, marking the highest level ever recorded.
The concentrations of methane and nitrous oxide also reached record highs.
The World Meteorological Organization stated that the concentration of greenhouse gases has reached 1.5 times that of pre-industrial levels.
In particular, it was analyzed that the increase in greenhouse gases last year was influenced by record-breaking wildfires that swept across the globe.
Due to the effects of global warming, prolonged large wildfires occurred in Canada, Australia, and other regions, with carbon emissions from wildfires increasing by about 16% compared to the average.
[Ko Barrett/WMO Deputy Secretary-General: "The bulletin warns that the carbon cycle risk becomes a potentially vicious cycle. In the near future, the climate change feedbacks could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of greenhouse gases."]
In fact, recent research by South Korean scientists examining the risk of wildfires based on carbon dioxide concentration found that as the concentration increases, the likelihood of wildfires occurring in most parts of the world rises sharply.
[Min Seung-ki/Professor, Environmental Science & Engineering Division at POSTECH: "As carbon dioxide increases, temperatures rise and soil moisture decreases significantly, leading to drier conditions. The conditions conducive to wildfires are increasing, along with the corresponding areas and seasons."]
Experts agree that the climate crisis is reaching an irreversible level and that stronger efforts to reduce greenhouse gases must be pursued.
This is KBS News Kim Se-hyun.
Last year, the global concentration of greenhouse gases reached a record high once again.
It has been analyzed that large wildfires caused by the effects of global warming around the world were the main reason, and the World Meteorological Organization has warned that we are facing a vicious cycle.
Our weather expert Kim Se-hyun reports.
[Report]
Despite global reduction efforts, greenhouse gases have increased again.
The concentration of carbon dioxide, a representative greenhouse gas, was 420 ppm last year, an increase of 2.3 ppm from the previous year, marking the highest level ever recorded.
The concentrations of methane and nitrous oxide also reached record highs.
The World Meteorological Organization stated that the concentration of greenhouse gases has reached 1.5 times that of pre-industrial levels.
In particular, it was analyzed that the increase in greenhouse gases last year was influenced by record-breaking wildfires that swept across the globe.
Due to the effects of global warming, prolonged large wildfires occurred in Canada, Australia, and other regions, with carbon emissions from wildfires increasing by about 16% compared to the average.
[Ko Barrett/WMO Deputy Secretary-General: "The bulletin warns that the carbon cycle risk becomes a potentially vicious cycle. In the near future, the climate change feedbacks could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of greenhouse gases."]
In fact, recent research by South Korean scientists examining the risk of wildfires based on carbon dioxide concentration found that as the concentration increases, the likelihood of wildfires occurring in most parts of the world rises sharply.
[Min Seung-ki/Professor, Environmental Science & Engineering Division at POSTECH: "As carbon dioxide increases, temperatures rise and soil moisture decreases significantly, leading to drier conditions. The conditions conducive to wildfires are increasing, along with the corresponding areas and seasons."]
Experts agree that the climate crisis is reaching an irreversible level and that stronger efforts to reduce greenhouse gases must be pursued.
This is KBS News Kim Se-hyun.
■ 제보하기
▷ 카카오톡 : 'KBS제보' 검색, 채널 추가
▷ 전화 : 02-781-1234, 4444
▷ 이메일 : kbs1234@kbs.co.kr
▷ 유튜브, 네이버, 카카오에서도 KBS뉴스를 구독해주세요!
- Record high greenhouse gas emissions linked to large wildfires driven by global warming
-
- 입력 2024-10-28 23:48:49

[Anchor]
Last year, the global concentration of greenhouse gases reached a record high once again.
It has been analyzed that large wildfires caused by the effects of global warming around the world were the main reason, and the World Meteorological Organization has warned that we are facing a vicious cycle.
Our weather expert Kim Se-hyun reports.
[Report]
Despite global reduction efforts, greenhouse gases have increased again.
The concentration of carbon dioxide, a representative greenhouse gas, was 420 ppm last year, an increase of 2.3 ppm from the previous year, marking the highest level ever recorded.
The concentrations of methane and nitrous oxide also reached record highs.
The World Meteorological Organization stated that the concentration of greenhouse gases has reached 1.5 times that of pre-industrial levels.
In particular, it was analyzed that the increase in greenhouse gases last year was influenced by record-breaking wildfires that swept across the globe.
Due to the effects of global warming, prolonged large wildfires occurred in Canada, Australia, and other regions, with carbon emissions from wildfires increasing by about 16% compared to the average.
[Ko Barrett/WMO Deputy Secretary-General: "The bulletin warns that the carbon cycle risk becomes a potentially vicious cycle. In the near future, the climate change feedbacks could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of greenhouse gases."]
In fact, recent research by South Korean scientists examining the risk of wildfires based on carbon dioxide concentration found that as the concentration increases, the likelihood of wildfires occurring in most parts of the world rises sharply.
[Min Seung-ki/Professor, Environmental Science & Engineering Division at POSTECH: "As carbon dioxide increases, temperatures rise and soil moisture decreases significantly, leading to drier conditions. The conditions conducive to wildfires are increasing, along with the corresponding areas and seasons."]
Experts agree that the climate crisis is reaching an irreversible level and that stronger efforts to reduce greenhouse gases must be pursued.
This is KBS News Kim Se-hyun.
Last year, the global concentration of greenhouse gases reached a record high once again.
It has been analyzed that large wildfires caused by the effects of global warming around the world were the main reason, and the World Meteorological Organization has warned that we are facing a vicious cycle.
Our weather expert Kim Se-hyun reports.
[Report]
Despite global reduction efforts, greenhouse gases have increased again.
The concentration of carbon dioxide, a representative greenhouse gas, was 420 ppm last year, an increase of 2.3 ppm from the previous year, marking the highest level ever recorded.
The concentrations of methane and nitrous oxide also reached record highs.
The World Meteorological Organization stated that the concentration of greenhouse gases has reached 1.5 times that of pre-industrial levels.
In particular, it was analyzed that the increase in greenhouse gases last year was influenced by record-breaking wildfires that swept across the globe.
Due to the effects of global warming, prolonged large wildfires occurred in Canada, Australia, and other regions, with carbon emissions from wildfires increasing by about 16% compared to the average.
[Ko Barrett/WMO Deputy Secretary-General: "The bulletin warns that the carbon cycle risk becomes a potentially vicious cycle. In the near future, the climate change feedbacks could cause ecosystems to become larger sources of greenhouse gases."]
In fact, recent research by South Korean scientists examining the risk of wildfires based on carbon dioxide concentration found that as the concentration increases, the likelihood of wildfires occurring in most parts of the world rises sharply.
[Min Seung-ki/Professor, Environmental Science & Engineering Division at POSTECH: "As carbon dioxide increases, temperatures rise and soil moisture decreases significantly, leading to drier conditions. The conditions conducive to wildfires are increasing, along with the corresponding areas and seasons."]
Experts agree that the climate crisis is reaching an irreversible level and that stronger efforts to reduce greenhouse gases must be pursued.
This is KBS News Kim Se-hyun.
-
-

김세현 기자 weather@kbs.co.kr
김세현 기자의 기사 모음
-
이 기사가 좋으셨다면
-
좋아요
0
-
응원해요
0
-
후속 원해요
0













이 기사에 대한 의견을 남겨주세요.