FUTURE OF KOREA’S SECONDARY BATTERY MARKET
입력 2022.11.21 (15:28)
수정 2022.11.21 (16:45)
읽어주기 기능은 크롬기반의
브라우저에서만 사용하실 수 있습니다.
[Anchor Lead]
As demand for electric vehicles rises worldwide, the secondary battery sector is also growing rapidly. With Korea holding a competitive edge in the industry, secondary batteries are expected to become a new growth engine for the Korean economy. However, there are also concerns about a possible crisis in the rapidly changing business environment.
[Pkg]
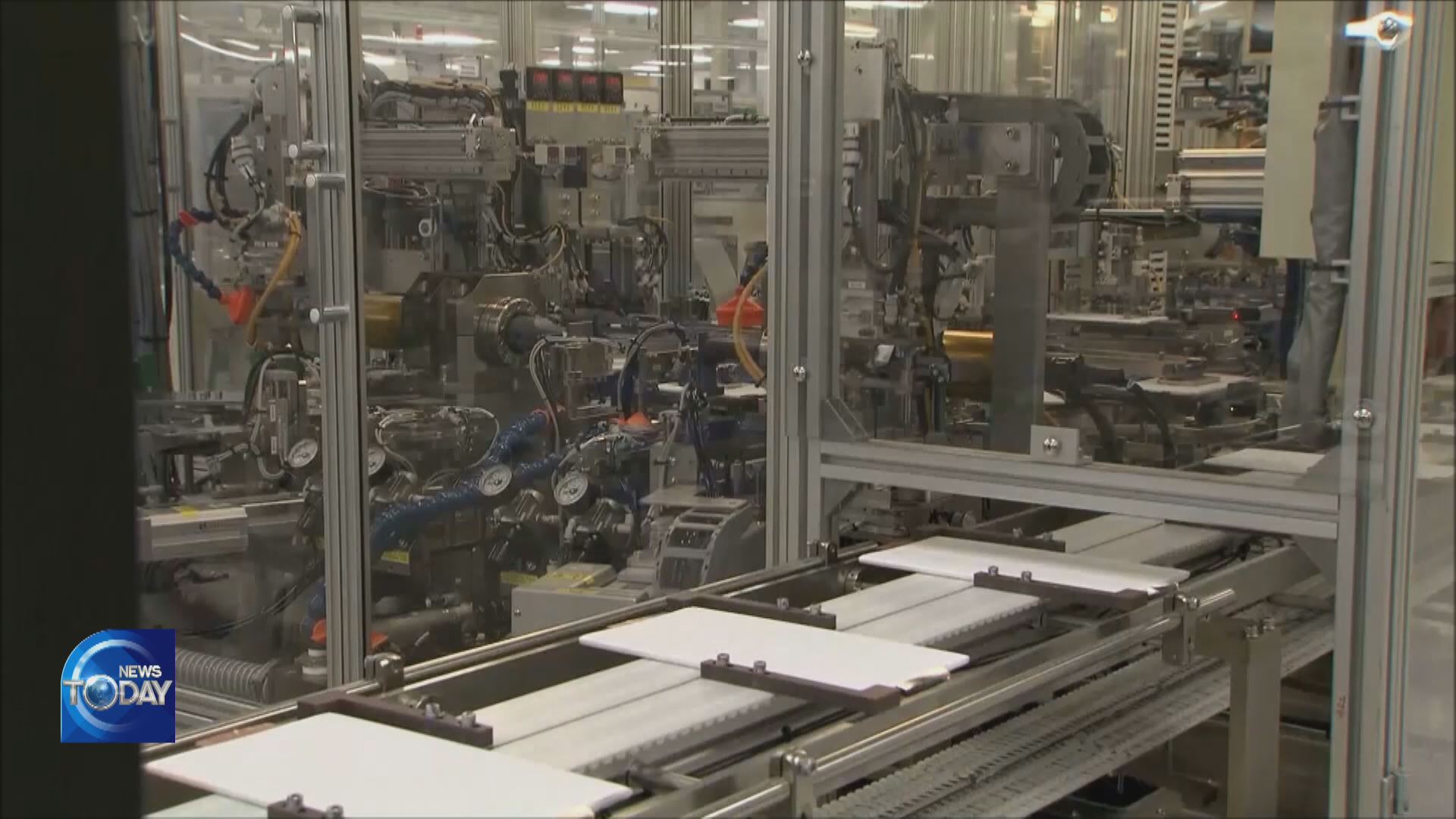
A salt lake in Salta, Argentina. This is where a Korean conglomerate extracts lithium to produce secondary batteries for electric vehicles. Demand for lithium is rising lately on the growing demand for electric cars. This firm is preparing to import the extracted lithium to Korea for processing. That's because processing it in Korea is now inevitable under the Inflation Reduction Act, which only gives benefits when more than 40 percent of minerals are processed in the U.S. or countries that have FTAs with the U.S., like South Korea. Meanwhile, Korean businesses' reliance on China in terms of lithium processing reaches 81 percent. They stand a high chance of losing competitiveness in the U.S., the largest EV market, unless they diversify their supply chain. Things could become even tougher because Europe is also preparing to enact a law to reduce reliance on Chinese materials. Major Korean battery makers are increasingly turning their eyes to Australia and Canada. But they face many challenges.
[Soundbite] Chung Kwang-ha(Korea Industry Alliance Forum) : "Developing minerals overseas requires massive capital and cooperation from other countries. It also entails a high risk of failure. The private sector cannot do it alone."
The government has decided to provide three trillion won over five years to help domestic businesses establish a presence in overseas mineral markets.
[Soundbite] Lee Chang-yang(Industry Minister) : "We will spare no resources to provide businesses with opportunities for new projects, financing and consulting to help them stably secure minerals."
As of late 2021, Korea's top-three secondary battery manufacturers had acquired orders worth 560 trillion won. With the secondary battery market predicted to grow by tenfold in the next decade, expectations are rising that secondary batteries could become a new growth engine for the Korean economy.
As demand for electric vehicles rises worldwide, the secondary battery sector is also growing rapidly. With Korea holding a competitive edge in the industry, secondary batteries are expected to become a new growth engine for the Korean economy. However, there are also concerns about a possible crisis in the rapidly changing business environment.
[Pkg]
A salt lake in Salta, Argentina. This is where a Korean conglomerate extracts lithium to produce secondary batteries for electric vehicles. Demand for lithium is rising lately on the growing demand for electric cars. This firm is preparing to import the extracted lithium to Korea for processing. That's because processing it in Korea is now inevitable under the Inflation Reduction Act, which only gives benefits when more than 40 percent of minerals are processed in the U.S. or countries that have FTAs with the U.S., like South Korea. Meanwhile, Korean businesses' reliance on China in terms of lithium processing reaches 81 percent. They stand a high chance of losing competitiveness in the U.S., the largest EV market, unless they diversify their supply chain. Things could become even tougher because Europe is also preparing to enact a law to reduce reliance on Chinese materials. Major Korean battery makers are increasingly turning their eyes to Australia and Canada. But they face many challenges.
[Soundbite] Chung Kwang-ha(Korea Industry Alliance Forum) : "Developing minerals overseas requires massive capital and cooperation from other countries. It also entails a high risk of failure. The private sector cannot do it alone."
The government has decided to provide three trillion won over five years to help domestic businesses establish a presence in overseas mineral markets.
[Soundbite] Lee Chang-yang(Industry Minister) : "We will spare no resources to provide businesses with opportunities for new projects, financing and consulting to help them stably secure minerals."
As of late 2021, Korea's top-three secondary battery manufacturers had acquired orders worth 560 trillion won. With the secondary battery market predicted to grow by tenfold in the next decade, expectations are rising that secondary batteries could become a new growth engine for the Korean economy.
■ 제보하기
▷ 카카오톡 : 'KBS제보' 검색, 채널 추가
▷ 전화 : 02-781-1234, 4444
▷ 이메일 : kbs1234@kbs.co.kr
▷ 유튜브, 네이버, 카카오에서도 KBS뉴스를 구독해주세요!
- FUTURE OF KOREA’S SECONDARY BATTERY MARKET
-
- 입력 2022-11-21 15:28:25
- 수정2022-11-21 16:45:13

[Anchor Lead]
As demand for electric vehicles rises worldwide, the secondary battery sector is also growing rapidly. With Korea holding a competitive edge in the industry, secondary batteries are expected to become a new growth engine for the Korean economy. However, there are also concerns about a possible crisis in the rapidly changing business environment.
[Pkg]
A salt lake in Salta, Argentina. This is where a Korean conglomerate extracts lithium to produce secondary batteries for electric vehicles. Demand for lithium is rising lately on the growing demand for electric cars. This firm is preparing to import the extracted lithium to Korea for processing. That's because processing it in Korea is now inevitable under the Inflation Reduction Act, which only gives benefits when more than 40 percent of minerals are processed in the U.S. or countries that have FTAs with the U.S., like South Korea. Meanwhile, Korean businesses' reliance on China in terms of lithium processing reaches 81 percent. They stand a high chance of losing competitiveness in the U.S., the largest EV market, unless they diversify their supply chain. Things could become even tougher because Europe is also preparing to enact a law to reduce reliance on Chinese materials. Major Korean battery makers are increasingly turning their eyes to Australia and Canada. But they face many challenges.
[Soundbite] Chung Kwang-ha(Korea Industry Alliance Forum) : "Developing minerals overseas requires massive capital and cooperation from other countries. It also entails a high risk of failure. The private sector cannot do it alone."
The government has decided to provide three trillion won over five years to help domestic businesses establish a presence in overseas mineral markets.
[Soundbite] Lee Chang-yang(Industry Minister) : "We will spare no resources to provide businesses with opportunities for new projects, financing and consulting to help them stably secure minerals."
As of late 2021, Korea's top-three secondary battery manufacturers had acquired orders worth 560 trillion won. With the secondary battery market predicted to grow by tenfold in the next decade, expectations are rising that secondary batteries could become a new growth engine for the Korean economy.
As demand for electric vehicles rises worldwide, the secondary battery sector is also growing rapidly. With Korea holding a competitive edge in the industry, secondary batteries are expected to become a new growth engine for the Korean economy. However, there are also concerns about a possible crisis in the rapidly changing business environment.
[Pkg]
A salt lake in Salta, Argentina. This is where a Korean conglomerate extracts lithium to produce secondary batteries for electric vehicles. Demand for lithium is rising lately on the growing demand for electric cars. This firm is preparing to import the extracted lithium to Korea for processing. That's because processing it in Korea is now inevitable under the Inflation Reduction Act, which only gives benefits when more than 40 percent of minerals are processed in the U.S. or countries that have FTAs with the U.S., like South Korea. Meanwhile, Korean businesses' reliance on China in terms of lithium processing reaches 81 percent. They stand a high chance of losing competitiveness in the U.S., the largest EV market, unless they diversify their supply chain. Things could become even tougher because Europe is also preparing to enact a law to reduce reliance on Chinese materials. Major Korean battery makers are increasingly turning their eyes to Australia and Canada. But they face many challenges.
[Soundbite] Chung Kwang-ha(Korea Industry Alliance Forum) : "Developing minerals overseas requires massive capital and cooperation from other countries. It also entails a high risk of failure. The private sector cannot do it alone."
The government has decided to provide three trillion won over five years to help domestic businesses establish a presence in overseas mineral markets.
[Soundbite] Lee Chang-yang(Industry Minister) : "We will spare no resources to provide businesses with opportunities for new projects, financing and consulting to help them stably secure minerals."
As of late 2021, Korea's top-three secondary battery manufacturers had acquired orders worth 560 trillion won. With the secondary battery market predicted to grow by tenfold in the next decade, expectations are rising that secondary batteries could become a new growth engine for the Korean economy.
이 기사가 좋으셨다면
-
좋아요
0
-
응원해요
0
-
후속 원해요
0














이 기사에 대한 의견을 남겨주세요.